America
Ferrets, Ravens & Weasels
Radar Countermeasures and SAM suppression
Overview
|



|
US Army
US Navy
US Air Force
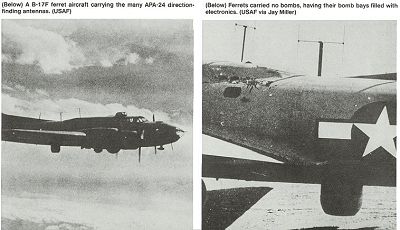 |
| B-17F Ferret |
Ferret I
- 6 March 1943.
- Consolidated B-24D Liberator modified with APR-4 search receivers.
- Operational tests against Japanese Mark 1 Model 1 radar at Kiska Island in Aleutians.
Ferret II
- Prototype testbed, no information.
Ferret III, IV, V, VI
- 21 April 1943 / May 1943 to September 1943 / 1944.
- Four Boeing B-17F Flying Fortresses modified with APA-24 and other electronic gear in bomb bay in place of bombs.
- 16th Reconnaissance Squadron, Foch Field, Tunisia.
- Operational RCM missions against German radar installations in Sicily, Sardinia, Corsica, Italy and southern France.
- Data gathered used for amphibious assaults (Husky, Avalanche, Shingle, Dragoon) and bombing missions for 15th Air Force.
- Additional 35 aircraft modified for Ferret mission.
- Known serials: 42-29644, B-17F-65-BO Ferret III.
 |
| B-24H Ferret "Little Girl" |
Ravens in the Pacific
- 1944 - 1945.
- Various Consolidated B-24 Liberator and Boeing B-29 Superfortress bombers modified with detection gear.
- Operations over Hong Kong - Canton, Formosa, the Pescadores, Hainan Island, China.
- One B-29 in each bomber squadron was equipped with receivers, pulse analyzer and preset jammers.
- Four squadrons of B-29 Ferrets used for passive RCM, monitoring, locating and jamming Japanese radars.
- Targets attacked by 20th Air Force or squadrons (incl. 499th Bomb Squadron) flying North American B-25 Mitchell gunships equipped with homing sensors.
Post-war Ferrets
- August - September 1946.
- B-17G Ferret, equipped with AN/APR-4 & AN/APR-5 search receivers, AN/APA-10 & AN/APA-11 pulse analyzers, Hewlett-Packard audio oscillator,
associated pulse repetition frequency analyzer and ink-on-tape recorder, used by 311th Reconnaissance Wing in attempt to locate possible Soviet radar sites in
nothern Greenland.
- August 1946.
- Two USAFE B-17 Ferrets equipped with AN/APR-4 search receivers and AN/APA-17 & AN/APA-24 D/F antennas used to find Yugoslavian radar-controlled
anti-aircraft gun site (which had earlier shot down an American C-47).
- Led to creation of 7499th Squadron, electronic reconnaissance along Soviet borders.
- January 1947.
- B-29 Ferret modified for ELINT:
- All armament removed.
- Rear pressurized area converted into electronic intercept station.
- Additional fuel in bomb bay.
- Thirteen total in crew: pilot, co-pilot, three navigators, radio operator, flight engineer, six electronics operators (Ravens: three search & analysis,
three direction finding).
- B-29 No. 812 Sitting Duck.
- Deployed to Ladd AFB, Alaska and tasked to find Soviet radar sites on Siberian coast.
- Continued development of ELINT mission to create Soviet EOB (electronic order of battle).
Korean War Ferrets
- Douglas B-26 Invaders equipped with homing receivers, including APA-24.
- Tactics: beam-riding until radar site visually acquired, then attacking with guns, rockets or bombs.
- Unarmed TB-25J "hunters" sometimes used in conjunction with B-26 "killers."
- RCM mission left to individual bomb groups for most of the war.
- Late war, RCM mission given to 11th Tactical Reconnaissance Squadron, 67th Tactical Reconnaissance Wing, Kimpo, using RB-26, WB-26.
Post-Korean War Ferrets
- 1954.
- 9th Tactical Reconnaissance Squadron, Shaw AFB, established.
- Douglas B-26 Invader.
- Mission:
- Locate and destroy enemy radar.
- Locate enemy radar and direct strike aircraft to destroy.
- Later re-equipped with unarmed Douglas RB-66 Destroyer.
 |
| North American F-100F Super Sabre (Wild Weasel I), s/n 58-1221 |
Viet Nam: Wild Weasel I
- Exercise Goldfire, 1964:
- Several North American F-100F Super Sabre fighters equipped with QRC-253-2 homing system to detect MIM-23 Hawk SAM.
- 3 August 1965:
- Committee led by Brigadier General K. C. Dempster to determine effective counter to North Vietnamese SAMs.
- Project Ferret, re-named Project Wild Weasel to avoid conflict with original World War II ferrets, led by John Paup.
- Four modified North American F-100F Super Sabres, modified by North American (modification 1778).
- Known serials:
- F-100F-20-NA s/n 58-1212 (replacement for 58-1231).
- F-100F-20-NA s/n 58-1221 (one of first four Wild Weasel a/c).
- F-100F-20-NA s/n 58-1226 (one of first four Wild Weasel a/c).
- F-100F-20-NA s/n 58-1227 (one of first four Wild Weasel a/c).
- F-100F-20-NA s/n 58-1231 (one of first four Wild Weasel a/c).
- F-100F-20-NA s/n 58-1232.
- Wiring and other non-essential systems removed, Applied Technology Inc. electronic gear installed:
- APR-25 Vector IV Radar Homing and Warning system.
- IR-133 panoramic receiver and signal analysis.
- APR-26 WR-300 Launch Warning Receiver.
- Mohawk Midgetape 400 tape recorder.
- KA-60 strike camera on one aircraft only.
- Log periodic antennas on nose instead of IR-133 on 58-1231.
- 1965: flight testing at Edwards AFB.
- 4 September 1965: testing and training moved to Eglin AFB, FL.
- 21 November 1965: deployed to Korat, Thailand, for operational testing.
- Operations with 388th Tactical Fighter Wing, as 6234th Tactical Fighter Wing (Wild Weasel Detachment).
- 28 November 1965: orientation flights with Douglas RB-66 along North Vietnamese border, Route Pack 2 & 3.
- 1 December 1965: first combat mission, code name Iron Hand; two F-100F Wild Weasels leading flights of F-105 Thunderchiefs.
- Armament: two 24-shot LAU-3 rocket pods with HEAT or HEAP warheads for target marking and attack, plus 20 mm cannon.
- 20 December 1965: first combat loss, F-100F s/n 58-1231 shot down, pilot (John Pitchford) POW, EWO (Bob Trier) KIA.
- 22 December 1965: first SAM site kill, F-100F s/n 58-1226, rail yard at Yen Bai, pilot Al Lamb, EWO Jack Donovan.
- 13 March 1966: F-100F s/n 58-1221 lost in training accident, engine failure.
- 23 March 1966: F-100F s/n 58-1212 shot down, crew KIA (Clyde Dawson, Donald Clark).
- March 1966: AGM-45 Shrike ARM.
- 18 April 1966: first combat use of Shrike.
- 11 July 1966: end of operational deployment of Wild Weasel I.

Wild Weasel I-A
- Two Republic F-105D Thunderchief modified and tested with RHAW, AZ/EL.
Wild Weasel II
- One Republic F-105F modified and tested with Bendix RHAW equipment.
- Cancelled in favor of ATI RHAW system.
 |
Republic F-105G Thunderchief (Wild Weasel III) s/n 63-8328,
561st or 562nd TFS, 35th TFW, George AFB |
Wild Weasel III
- Improved Wild Weasel program using higher-performance aircraft and integrating lessons learned from Wild Weasel I program.
- One initial prototype Republic EF-105F Thunderchief conversion:
- F-105F-1-RE s/n 62-4416.
- First flight 15 January 1966.
- Electronic and other gear:
- APR-25(V) (ATI Vector 4) RHAW.
- IR-133C panoramic scan receiver.
- APR-26 (WR-300) Launch Warning Receiver.
- AZ-EL system.
- Stancil-Hoffman two-channel tape recorder.
- KA-71 combat motion picture camera.
- Standard F-105F armament, plus AGM-45 Shrike capability.
- EF-105F designation was unofficial.
- Ten additional EF-105F conversions, known serials:
- F-105F-1-RE s/n 63-8262.
- F-105F-1-RE s/n 63-8273.
- F-105F-1-RE s/n 63-8285 Honey.
- F-105F-1-RE s/n 63-8286.
- F-105F-1-RE s/n 63-8301 Jinkin' Josie.
- F-105F-1-RE s/n 63-8302 half a yard.
- F-105F-1-RE s/n 63-8317 HALF FAST.
- F-105F-1-RE s/n 63-8330.
- May 1966: all EF-105F (except first prototype) deployed to Korat, Thailand, for operational testing; four modified with North American SEE-SAM(B) passive
warning system.
- Operated with 13th Tactical Fighter Squadron, 388th Tactical Fighter Wing.
- 3 June 1966: first orientation mission.
- 7 June 1966: first radar site kill.
- August 1966: additional EF-105F detachment with 354th Tactical Fighter Squadron, Takhli, Thailand.
- 23 July 1966: first combat loss (five total).
- Summer 1967: six EF-105F from combat units and four EF-105F from Nellis AFB modified with AGM-78A-1 Standard ARM
capability and deployed to 357th Tactical Fighter Squadron for combat testing; one aircraft (s/n 62-4441) lost in
combat before modification.
- 1966-1967: 7th Air Force orders all F-105s to carry at least one AIM-9 Sidewinder on all combat missions.
- 1967: 7th Air Force revise order to require all tactical combat aircraft flying missions over North Viet Nam to
carry ECM pods, thus reducing Wild Weasel combat capability:
- Normal combat load: two AGM-45 Shrike and two CBUs under wings and one 600 gal. drop tank on centerline.
- Alternative combat load: two AGM-45 Shrike and two 450 gal. drop tanks under wings and four-six bombs or CBUs
on centerline.
- Reduced combat load: one AGM-45 Shrike, one ECM pod, two CBUs, one 600 gal. drop tank.
- Fall 1967: Continued equipment improvements and need for increased ordnance capability lead to development of F-105G by Republic,
Westinghouse and USAF Tactical Air Warfare Center.
- 8 March 1968: first EF-105F w/ AGM-78 combat mission.
- April 1968: Initial F-105G combat deployment.
- 10 May 1968: first EF-105F combat firing of AGM-78.
- Continued EF-105F equipment updates:
- ATI RHAW improvements.
- KA-60 strike camera, later KA-71.
- ATI Pointer System into optical sight homing display.
- Loral QRC-317A SEE-SAMS system, later updated as ALR-31.
- F-105G updgrades (86 conversions from F-105F/EF-105F):
- Westinghouse ALQ-101 ECM pod mounted on fuselage sides, initially as QRC-380, standardized as ALQ-105 ECM system;
first tested in F-105F s/n 62-4414; installed on all F-105F/G from 1971.
- APR-35/36 RHAW system (replaced APR-25/26 and ER-142).
- ALR-31 SEE-SAMS (replaced QRC-317A).
- APR-37.
- QRC-373 jammer.
- AGM-78B (Mod 1).
- Typical combat loads:
- Two AGM-45 Shrike ARMs on two outboard underwing stations; one AGM-78B Standard ARM on right inboard
underwing station, one 450 gal. drop tank on left inboard underwing station, or
- Two AGM-45 and two AGM-78 ARMs underwings and one 600 gal. drop tank under centerline.
- Known F-105G serial numbers:
- F-105F-1-RE 62-4416.
- F-105F-1-RE 62-4422.
- F-105F-1-RE 62-4423.
- F-105F-1-RE 62-4424.
- F-105F-1-RE 62-4425.
- F-105F-1-RE 62-4427.
- F-105F-1-RE 62-4428.
- F-105F-1-RE 62-4432.
- F-105F-1-RE 62-4434.
- F-105F-1-RE 62-4436.
- F-105F-1-RE 62-4438.
- F-105F-1-RE 62-4439.
- F-105F-1-RE 62-4440.
- F-105F-1-RE 62-4442.
- F-105F-1-RE 62-4443.
- F-105F-1-RE 62-4444.
- F-105F-1-RE 62-4446.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8265.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8266.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8274.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8275.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8276.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8278.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8284.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8285.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8291.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8292.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8296.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8300.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8301.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8302.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8303.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8304.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8305.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8306.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8307.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8311.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8313.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8316.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8318.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8319.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8320.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8321.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8326.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8327.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8328.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8332.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8333.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8334.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8336.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8339.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8340.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8342.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8345.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8347.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8350.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8350.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8351.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8355.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8359.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8360.
- F-105F-1-RE 63-8363.
 |
| Republic F-105G Thunderchief (Wild Weasel III) s/n 62-4428 |
Willie Weasel College 4537th Fighter Weapons School
- Established by Wild Weasel I crews at Nellis AFB, February 1966.
- Dean: Col. Garry Williard, Jr.
- Instructors:
- Maj. Jack Donovan.
- Maj. Walt Lifsey.
- Maj. Ed White.
- Maj. Al Lamb.
- Maj. Maury Fricke.
- Maj. Shep Kerr.
- Maj. John Mojica.
- Maj. Frank O'Donnell.
- Maj. Rick Morgan.
- Crew selection, pilot/EWO pairing.
- Initially four-six week courses, some later up to twelve weeks long.
- Twenty-one missions against simulated Soviet radar sites at St. George or Hawthorne Ranges in Utah.
- Flight and ground training.
- Three North American T-39A Sabreliners modified as T-39F "Teeny Weeny Weasel" trainers:
- Passenger seats removed.
- EF-105F equipment installed, including APR-25 RHAW, IR-133C panoramic receiver, APR-26 LWR and
Loral QRC-317A SEE-SAMS; RHAW and AZ-EL antennas on nose/tail.
- Three EWO training consoles installed.
- Known serial numbers:
- CT-39A-1-NA 59-2872, NAA c/n 265-5.
- T-39-A-1-NA 60-3507, NAA c/n 265-35.
 |
| USN LTV A-7E-6-CV Corsair II (BuNo 157454) with AGM-45 Shrike |
Iron Hand: US Navy SAM suppression in Viet Nam
- Summer 1967.
- Several modified Grumman A-6A Intruders.
- Equipment included ATI ER-142 receiver system, Bendix APS-107B RHAW
- AGM-78 Standard ARM capability.
- A-6B: A-6A SEAD field conversions:
- Equipment included:
- AS-2839/ALP-55 Warning Antennas.
- AS-2Q50 Homing Antennas.
- APL PAT/ARM system.
- AGM-78A Standard ARM.
- IBM TIAS.
- Known serial numbers (19 A-6A conversions):
- BuNo 149944, c/n I-25.
- BuNo 149949, c/n I-30.
- BuNo 149955, c/n I-36.
- BuNo 149957, c/n I-38.
- BuNo 151558, c/n I-40.
- BuNo 151559, c/n I-41.
- BuNo 151560, c/n I-42.
- BuNo 151561, c/n I-43.
- BuNo 151562, c/n I-44.
- BuNo 151563, c/n I-45.
- BuNo 151564, c/n I-46.
- BuNo 151565, c/n I-47.
- BuNo 151591, c/n I-73.
- BuNo 151820, c/n I-123.
- BuNo 152616, c/n I-164.
- BuNo 152617, c/n I-165.
- BuNo 154046/154099 (54 cancelled conversions).
- BuNo 155628, c/n I-354.
- BuNo 155629, c/n I-355.
- BuNo 155630, c/n I-356.
- August 1967: first A-6B delivery.
- 26 August 1968: first flight of first aircraft (BuNo 155628) of second batch of A-6B conversions.
- August 1970: final A-6B delivery.
December 1975 - 1979: 14 surviving A-6B converted to A-6E.
- Unknown number of Douglas A-4F Skyhawks also convered for SAM suppression for use on smaller aircraft carriers;
equipment included Bendix APS-107B RHAW.
- Some Vought A-7E Corsair II also used for SAM suppression with APS-107 RHAW.
Wild Weasel IV-A
- 1966-1968.
- Planned successor to F-105 Wild Weasel utilizing McDonnell Douglas F-4C Phantom II.
- Due to shortage of internal space in F-4, some equipment mounted in external pods.
- Equipment:
- Itek/ATI APR-25, APR-26 RHAW (internal).
- IR-133 panoramic receiver (external pod in right rear AIM-7 Sparrow recess).
- All AIM-7 Sparrow AAM-associated equipment and wiring removed.
- Incompatibility between existing and new wiring and vibration problems led to prolonged development time.
- Number of test aircraft conversions and serial numbers unknown; development revised under Wild Weasel IV-C.
Wild Weasel IV-B
- Two McDonnell Douglas F-4D Phantom II testbeds.
- Serial numbers:
- F-4D-27-MC 65-0657.
- F-4D-27-MC 65-0660.
- Equipment:
- Bendix APS-107 RHAW, proved to be unreliable and erratic for Wild Weasel combat missions, but
standardized for F-4D.
- ER-142 panoramic receiver.
- AGM-45 Shrike and AGM-78 Standard ARM capability.
- Other F-4D test aircraft:
- F-4D-27-MC s/n 65-0644, c/n 1635, used to test AGM-78.
- Several (s/n unknown) used to test AGM-65 Maverick AGM.
- Two (F-4D-30-MC s/n 66-7635, c/n 2208 and s/n 66-7647, c/n 2226) used to test APR-38 Warning and Attack
System for F-4G development; unofficially? designated EF-4D.
Wild Weasel IV-C
- June 1968.
- Continued development of F-4C Wild Weasel, with all equipment internally mounted due to vibration problems with
pod-mounted equipment under Wild Weasel IV-A program.
- Equipment included:
- APR-25 and APR-26 RHAW.
- ER-142 panoramic receiver.
- No AGM-78 Standard ARM capability due to lack of space for necessary equipment.
- 36 F-4C conversions to EF-4C (unofficial designation?), known block numbers and serial numbers:
- F-4C-16-MC 63-7423.
- F-4C-16-MC 63-7433.
- F-4C-16-MC 63-7437.
- F-4C-16-MC 63-7440.
- F-4C-17-MC 63-7443.
- F-4C-17-MC 63-7447.
- F-4C-17-MC 63-7452.
- F-4C-17-MC 63-7459.
- F-4C-17-MC 63-7462.
- F-4C-17-MC 63-7467.
- F-4C-18-MC 63-7470.
- F-4C-18-MC 63-7474.
- F-4C-18-MC 63-7478.
- F-4C-18-MC 63-7481.
- F-4C-18-MC 63-7508.
- F-4C-18-MC 63-7512.
- F-4C-18-MC 63-7513.
- F-4C-19-MC 63-7565.
- F-4C-19-MC 63-7567.
- F-4C-19-MC 63-7574.
- F-4C-19-MC 63-7594.
- F-4C-19-MC 63-7596.
- F-4C-20-MC 63-7607, c/n 684.
- F-4C-20-MC 63-7615.
- F-4C-20-MC 63-7623.
- F-4C-22-MC 64-0675.
- F-4C-23-MC 64-0741.
- F-4C-23-MC 64-0757.
- F-4C-23-MC 64-0781.
- F-4C-23-MC 64-0787.
- F-4C-23-MC 64-0790.
- F-4C-23-MC 64-0791.
- F-4C-23-MC 64-0815.
- F-4C-24-MC 64-0840.
- F-4C-24-MC 64-0844.
- F-4C-24-MC 64-0847.
- Deployed 1969-1971 to 81st TFS, Spangdahlem AB, Germany and 67th TFS, Kadena AB, Okinawa.
- October 1972 - January 1973: 67th TFS deployed TDY to Korat RTAB, Thailand, for Operation Linebacker II.
- Typical armament: AGM-45 Shrike ARM, 750 lb GP bombs, CBUs.
- 1973: all F-4C Wild Weasels redeployed as follows:
- 67th TFS (12 aircraft).
- 81st TFS (12 aircraft).
- 35 TFW, George AFB, California (12 aircraft, used to transition F-105 Wild Weasel crews to F-4).
- 1973 equipment upgrades:
- ALR-46 digital RHAW (APR-36/37 replaced analog APR-25/-26).
- ALR-53 Countermeasures Receiver (replaced ER-142).
- Surviving aircraft replaced by F-4G and transferred to Indiana ANG, used for standard fighter role.
Wild Weasel 5 / Advanced Wild Weasel
- Ultimate Wild Weasel development.
- McDonnell Douglas F-4E Phantom II rebuilt as F-4G.
- Equipment:
- McDonnell Douglas APR-38 Radar Warning and Attack System.
- Modified General Electric Lead Computing Gunsight/Heads Up Display.
- Itek/ATI RHAW.
- Conrac Corporation airborne data tape recorder.
- Lear Siegler ARN-101 digital navigation and attack system later added.
- One YF-4E (s/n 65-0713, c/n 1761) fitted with mock-up installation of AN/APR-38.
- 116 F-4E Block 42/43/44/45 conversions:
- All aircraft brought up to latest F-4E standards, stripped and rebuilt
with Wild Weasel equipment installed internally, including in chin pod (replacing gun) and vertical tail fairing.
- Wiring replaced with coaxial cable developed for F-15 Eagle.
- Redesigned rear cockpit.
- Air-to-air combat capability retained.
- Known serial numbers:
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0236, c/n 3757 as F-4G.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0237, c/n 3758 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1998.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0238, c/n 3760 as F-4G; later convered to QF-4G.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0239, c/n 3761 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1998.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0240, as F-4G.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0241, c/n 3764 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1997.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0242, c/n 3765 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1998.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0243, c/n 3767 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1997.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0244, c/n 3768 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1998.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0245, c/n 3769 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1998.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0246, c/n 3771 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1998.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0247, c/n 3772 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1997.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0248, c/n 3773 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1997.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0249, c/n 3775 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0250, c/n 3776 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1998.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0251, c/n 3778 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1998.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0252, as F-4G.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0253, c/n 3780 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0254, c/n 3782 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1998.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0255, c/n 3783 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1998.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0257, as F-4G.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0258, c/n 3787 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1998.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0259, c/n 3788 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1998.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0260, c/n 3790 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0261, c/n 3791 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1998.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0263, c/n 3794 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0264, c/n 3795 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1998.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0265, c/n 3797 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0267, c/n 3799 as F-4G.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0269, c/n 3802 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0270, c/n 3803 as F-4G.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0271, as F-4G.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0272, c/n 3806 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1998.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0273, c/n 3807 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1997.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0274, c/n 3809 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1998.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0275, c/n 3810 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0277, c/n 3813 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0278, c/n 3814 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1997.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0279, c/n 3815 as F-4G.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0280, as F-4G.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0281, c/n 3818 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1998.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0283, as F-4G.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0284, c/n 3822 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1998.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0285, c/n 3823 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1997.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0286, c/n 3825 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0290, c/n 3830 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1998.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0292, c/n 3832 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1998.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0293, as F-4G.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0297, as F-4G.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0297, c/n 3839 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-42-MC s/n 69-0303, c/n 3845 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-43-MC s/n 69-7201, c/n 3854 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1999.
- F-4E-43-MC s/n 69-7202, c/n 3855 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1996.
- F-4E-43-MC s/n 69-7204, c/n 3857 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1997.
- F-4E-43-MC s/n 69-7205, as F-4G.
- F-4E-43-MC s/n 69-7206, as F-4G.
- F-4E-43-MC s/n 69-7207, c/n 3862 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1998.
- F-4E-43-MC s/n 69-7208, as F-4G.
- F-4E-43-MC s/n 69-7209, c/n 3865 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1999.
- F-4E-43-MC s/n 69-7210, c/n 3866 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1998.
- F-4E-43-MC s/n 69-7211, c/n 3868 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1997.
- F-4E-43-MC s/n 69-7212, c/n 3869 as F-4G.
- F-4E-43-MC s/n 69-7213, as F-4G.
- F-4E-43-MC s/n 69-7214, c/n 3873 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-43-MC s/n 69-7215, as F-4G.
- F-4E-43-MC s/n 69-7216, c/n 3876 as F-4G.
- F-4E-43-MC s/n 69-7217, c/n 3877 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1997.
- F-4E-43-MC s/n 69-7218, c/n 3879 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-43-MC s/n 69-7219, as F-4G.
- F-4E-43-MC s/n 69-7228, c/n 3893 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1997.
- F-4E-43-MC s/n 69-7231, c/n 3898 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-43-MC s/n 69-7232, c/n 3900 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1997.
- F-4E-43-MC s/n 69-7233, c/n 3901 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-43-MC s/n 69-7234, c/n 3902 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1999.
- F-4E-43-MC s/n 69-7235, c/n 3903 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-43-MC s/n 69-7252, c/n 3929 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-43-MC s/n 69-7254, c/n 3932 as YF-4G prototype; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-43-MC s/n 69-7256, c/n 3935 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-43-MC s/n 69-7257, c/n 3936 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-43-MC s/n 69-7258, c/n 3939 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-43-MC s/n 69-7260, c/n 3943 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-44-MC s/n 69-7261, as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1996.
- F-4E-44-MC s/n 69-7262, c/n 3945 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-44-MC s/n 69-7263, c/n 3947 as F-4G; later to USAF Museum.
- F-4E-44-MC s/n 69-7267, c/n 3952 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1997.
- F-4E-44-MC s/n 69-7268, c/n 3955 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-44-MC s/n 69-7270, c/n 3957 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-44-MC s/n 69-7272, c/n 3960 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1998.
- F-4E-44-MC s/n 69-7286, c/n 3964 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-44-MC s/n 69-7287, c/n 3965 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-44-MC s/n 69-7288, c/n 3967 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-44-MC s/n 69-7289, c/n 3968 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-44-MC s/n 69-7290, c/n 3969 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-44-MC s/n 69-7291, c/n 3970 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-44-MC s/n 69-7293, c/n 3972 as F-4G.
- F-4E-44-MC s/n 69-7294, c/n 3974 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-44-MC s/n 69-7295, c/n 3975 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-44-MC s/n 69-7297, c/n 3978 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-44-MC s/n 69-7298, c/n 3978 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-44-MC s/n 69-7300, c/n 3980 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1996.
- F-4E-44-MC s/n 69-7301, as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-44-MC s/n 69-7303, c/n 3987; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-44-MC s/n 69-7546, c/n 3988; converted to QF-4G in 1998.
- F-4E-44-MC s/n 69-7550, as F-4G.
- F-4E-44-MC s/n 69-7551, as F-4G.
- F-4E-44-MC s/n 69-7556, c/n 4002 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1997.
- F-4E-44-MC s/n 69-7557, c/n 4004 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1998.
- F-4E-44-MC s/n 69-7558, c/n 4005 as F-4G.
- F-4E-44-MC s/n 69-7560, c/n 4009 as F-4G.
- F-4E-44-MC s/n 69-7561, c/n 4010 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-44-MC s/n 69-7566, c/n 4016 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-44-MC s/n 69-7571, as F-4G.
- F-4E-44-MC s/n 69-7572, c/n 4026 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1998.
- F-4E-44-MC s/n 69-7574, c/n 4028 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1998.
- F-4E-45-MC s/n 69-7579, c/n 4036 as F-4G; converted to QF-4G in 1998.
- F-4E-45-MC s/n 69-7580, c/n 4042 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-45-MC s/n 69-7581, c/n 4047 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-45-MC s/n 69-7582, c/n 4053 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-45-MC s/n 69-7583, c/n 4058 as F-4G; later converted to QF-4G.
- F-4E-45-MC s/n 69-7584, as F-4G.
- F-4E-45-MC s/n 69-7586, as F-4G.
- F-4E-45-MC s/n 69-7587, c/n 4079 as F-4G.
- F-4E-45-MC s/n 69-7855, as F-4G.
- Armament capability:
- External ordnance capability of F-4E, including AIM-9 Sidewinder and AIM-7 Sparrow.
- AGM-45C Shrike ARM.
- AGM-78D Standard ARM.
- AGM-88A HARM.
- AGM-65 Maverick AGM.
- ALQ-119V-17 or ALQ-131 ECM pod in forward left Sparrow bay.
- All training at 39th TFTS Wild Weasel school at George AFB.
- Operational deployment:
- 561st, 562nd TFS, George AFB.
- 81st TFS, 52nd TFW, Spangdahlem AB.
- 90th TFS, Clark AB, the Philippines.
- Deployed to Saudi Arabia in 1991 for Operation Desert Storm, with one loss.
- 1991 - 1996, aircraft from 561st and 562nd TFS transferred to Idaho ANG, Boise.
Wild Weasel 6 / F-4G Performance Update Program
- Late 1980's update of F-4G with APR-47 homing system.
Wild Weasel 7
- Planned F-15E (or possibly F-16B) Wild Weasel, cancelled.
F-16CJ/DJ Wild Weasel
- General Dynamics F-16C/D Block 50/52 Fighting Falcon.
- Standard F-16 fighter with SEAD capability; F-16CJ and F-16DJ are unofficial designations.
- Equipment:
- Northrop Grumman APG-68(V5) radar.
- HARM Avionics Launcher Interface Computer.
- Texas Instruments AN/ASQ-213 HARM Targeting System pod.
- Lockheed Martin (Loral) AN/ALR-56M RWR.
- AN/ALE-47 Group A chaff/flare dispenser.
- Known serial numbers: Joe Baugher: General Dynamics F-16A/B Block 50/52 Fighting Falcon
- Armament capability:
- Standard internal cannon and external ordnance capability of F-16C/D.
- AGM-88B HARM.
- AGM-137 TSSAM (cancelled).
- Operational deployment:
- 55th FS (July 1997 - present), 77th FS (3 January 1993 - present), 79th FS (1 January 1994 - present); 20th FW; Shaw AFB (1 January 1994 - present).
- 522nd FS; 27th FW; Cannon AFB (1998 - 21 December 2007; disbanded).
- 389th FS; 366th FW; Mountain Home AFB (1992 - 16 March 2007; converted to F-15E).
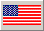 |
© 1998-2013, Robert Beechy
http://www.hud607.fire.prohosting.com/uncommon/reference/usa/sead.html
Originally posted 3 February 2013
Modified: 06/03/2017












